T
TACAS+
See Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus (TACAS+).
TAD
See technical architecture design (TAD).
TaleXus Vendor
A two-way multi resource revenue collection system that provides efficient revenue collection, enhanced data capture, and reporting for both electricity and gas utilities.
TALQ
An interoperability standard for the control and management of outdoor lighting and for interfacing outdoor lighting networks (OLN) with Central Management Software (CMS) applications.
TALQ Gateway
A Streetlight.Vision (SLV) software component that manages network traffic between Streetlight.Vision software and Advanced Metering Manager (AMM) application. TALQ Gateway is a required component for integrating Streetlight.Vision with an Electric UtilityIQ software stack.
TAM
See total available market (TAM).
tamper counter
An Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module component that increments whenever a tamper event occurs, such as a meter removal, cut cable, meter inversion, or reverse disk rotation. The types of tamper events that are detected depend on the ERT type.
Also called a tamper indicator.
tamper debounce
The amount of time, in milliseconds, required for the mechanical contact on a meter’s tilt switch to settle before a signal from the switch is considered to be valid on the Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module. This parameter is used to adjust the sensitivity of the meter removal tamper indicator.
tamper detector
An Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module component that senses when a meter has been tampered with. The types of tamper events that are detected vary according to the type of ERT module, and each detector detects a particular type of tamper. Examples of tamper events include meter removal, a cut cable, meter inversion, and reverse disk rotation.
Also called a tamper sensor.
tamper event code
Any alarms (including outage and restore) and tamper flags currently recorded by the meter and output as an event or alarm to the collection system. Events are typically delivered to the meter data management software as part of a response to a scheduled read request. Alarms are typically delivered as they occur.
tamper indicator
An Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module component that increments whenever a tamper event occurs, such as a meter removal, cut cable, meter inversion, or reverse disk rotation. The types of tamper events that are detected depends on the ERT type.
Also called a tamper counter.
tamper sensor
An Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module component that senses when a meter has been tampered with. The types of tamper events that are detected vary according to the type of ERT module, and each detector detects a particular type of tamper. Examples of tamper events include meter removal, a cut cable, meter inversion, and reverse disk rotation.
Also called a tamper detector.
tariff
A meter program on Secure Meters, Ltd meters.
tariff time slice
Several interlinked sub-elements including time slice intervals, day profiles, profile definitions, and allocation of day profiles that define the season and time of use (day/time). A tariff time slice defines which day profile to use on each day of each time slice interval.
TCO
See total cost of ownership (TCO).
TCP/IP
See Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
TCXO
See temperature-compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO).
TD8 DN20-25-32
A volumetric piston meter for residential cold-water metering.
TDEA Block Cipher
See Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA) Block Cipher.
TDMA
See time division multiple access (TDMA).
technical architecture design (TAD)
An artifact from a solution requirements workshop that contains the customer-specific hardware requirements. The technical architecture design (TAD) outlines the overall solution architecture designs for the proposed environment and provides a recommendation for hardware sizing. It also includes a diagram of the solution.
technical losses
Electricity losses due to expected loss between the generation source and the customer location meter. These can be due to normal losses through transmission and distribution, equipment failures, and non-optimized transmission loads and voltage.
Technical losses between 6 to 8% are considered normal. See also non-technical loss.
telemetry module
A low-power radio frequency device that attaches to a third-party device (for example, a rotary meter, a cathodic protection system, or gas line) to collect data. Itron telemetry modules allow remote measurement and reporting of utility system data not directly-related to meter reading and billing and transmit it to Itron data collection devices and systems.
Temetra
A cloud-based mobile meter data collection and management solution. All data is securely stored on servers that meet the ISO 27001 information security standard.
Temetra Analysis
An outcome that improves operational visibility, minimizes leaks, maximizes ROI on meter replacements, streamlines pressure management, reduces labor costs, optimizes network operations, and proactively improves the customer experience. Previously known as Water Operations Management (WOM).
Temetra Mobile
The Temetra software in an application format. This format is compatible with all Android-based mobile devices (V 4.4 or higher).
Temetra Reader
A mobile data collection application compatible with all Android™-based mobile devices (version 4.4 or higher).
Temetra web platform
A SaaS platform for data collection and management.
temperature-compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO)
A component of the SRead radio board used in Itron handheld computers and belt-clip radios. It supplies local oscillator and digital timing signals throughout the radio's components.
temperature compensation meter
A gas meter in which the measurement of gas volume is automatically corrected for the variation in gas temperature.
tenant
A representation of a customer, usually a utility, within a software application.
In the context of Tenant Management, a user can belong to one or more tenants, but the access token issued by Identity Server must refer to a single tenant context. A customer can have multiple tenants if needed. A single tenant query scope must always be specified in the user-authentication process.
tenant client
In the context of Tenant Management, a client with a pre-defined tenant context within the Itron Identity Service. Depending on its configuration, a standard client will provide a service principal with a set of requested tokens that contain either a consistent tenant context or no tenant context. A tenant client is intended to provide access tokens for different tenants but with similar claims. A separate tenant client should be created for each tenant.
Tenant Management
An identity service that provides user authentication and authorization for platform applications and provides a single location for managing tenants, applications, users, and roles. The service identifies authenticated users, applications, and tenants (utilities) and can determine the level of authority granted to a user or group of users. The service integrates with Azure Active Directory (AAD), allowing administrators to centrally manage accounts for an organization's users and to control user authentication with policies and other AAD configuration settings.
Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus (TACAS+)
A scalable, open-standard, Cisco security protocol that uses Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). This protocol separates the authorization functionality and provides granular access controls, which allows system administrators to specify what commands can be run on devices and who can run the commands. TACAS+ also encrypts the content of each packet. For more information, see tacas.net or cisco.com.
test mode
A mode of register operation. It allows testing of the register without altering billing data.
Th
See therm.
theft detection
An indicator that a meter was tampered with and a potential energy theft has occurred.
therm
The metered unit of natural gas energy. 1 therm equals 100,000 BTUs.
thin client
A computer or program that requests data, files, or services or accesses shared network resources from a server computer or program. Of the client classes, thin client, hybrid client, and rich client, a thin client relies upon the server the most heavily, for both data processing and data storage.
Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)
A collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations to standardize 3G (third generation) mobile phone system specifications. The specifications are those established by the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS).
3GPP should not be confused with Third Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2).
Third Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2)
A collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations to standardize 3G (third generation) mobile phone system specifications. The specifications are those established by the CDMA2000 family of standards.
3GPP2 is the standard body behind the competing 3G standard CDMA2000 that is the 3G upgrade to networks used mostly in the United States (and to some extent also in Japan, China, Canada, South Korea, and India). 3GPP2 should not be confused with Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
third-party configurator
The software components of the third-party that provides the meter configuration file in the required format.
third-party field tool
The software tool of the third-party meter partner used to communicate on the optical port of the device.
third-party firmware upgrader
The software components of the third-party that provides the firmware image files for the meter in the required format.
third-party meter
The Itron integrator partner’s device responsible for taking the required meter hardware measurements.
third-party meter manufacturing
The manufacturing facility of the third-party metering company.
TIBCO Conf files
Configuration files used with TIBCO EMS that contain a list of all Itron queues. When TIBCO EMS is started, it reads these files and initializes the queues.
TIBCO EMS
A third-party software component customized with Itron software to provide JMS functions for a number of Itron applications.
tier
Under tiered rate plans, the customer's cost per kilowatt hour (kWh) changes as more electricity is used within a billing period. Depending on your price plan, this cost can either go up or down at higher tiers.
tilt
A change in the direction or incline of a meter. A tamper tilt indicates that the meter has been illegally moved.
TIM
See translation interface module (TIM).
time division multiple access (TDMA)
A digital wireless communication transmission technology that allows many users to access a single radio frequency channel without interference. Each signal is divided into different time slots, which are uniquely assigned to users. With each user transmitting in rapid succession using their own time slot, multiple stations can share the same transmission medium while using only part of its frequency channel capacity.
time drift
The number of seconds a meter's time is different from the network time.
time of use (TOU)
An electricity billing rate where the rate varies by time. TOU metering divides the day into periods, such as 8:00 AM to 12:00 PM, 12:00 PM to 4:00 PM, and 4:00 PM to 8:00 AM. Each period has a corresponding rate, expressed in terms of $/kWh, where $ is the currency type configured for your rate plans (for example, $0.05/kWh). The rate is usually based on expected average cost (where prices are usually higher during peak periods) and is generally fixed for several months in advance. Rates can also change seasonally. HAN Communications Manager (HCM) supports 24 tiers per day.
time-of-use (TOU) rate
A rate with different unit prices for usage during different blocks of time, usually for a 24-hour period. TOU rates reflect the average cost of generating and delivering power during those time periods. Daily pricing blocks might include an on-peak, mid-peak, and off-peak price. In a time-of-use rate structure, higher prices are charged during utility peak-load times. Such rates can provide an incentive for consumers to curb power use during peak times.
time slice
The amount of processing time allocated to each user in a multi-user system. Also see tariff time slice.
time synchronization
To assure the proper operation of network devices, the calculation and storage of usage data, utility customer service, and accurate billing calculations, the meter clock synchronizes to the NIC clock and reports discrepancies to the Advanced Metering Manager (AMM) application resolve to the time on the Access Point.
time to live (TTL)
A mechanism, implemented as a counter or time stamp attached to or embedded in data, used to limit the lifespan of data on a network or within a caching system. When the prescribed event count is reached or timespan elapsed, the data is discarded or revalidated. Prescribing a TTL policy to data prevents the data from circulating indefinitely.
TLS
See transport layer security (TLS).
TLV
TMB
See Trap Messaging Bridge (TMB).
TMC
See total manufacturing cost (TMC).
TNS
See transparent network substrate (TNS).
tnsnames.ora
A file containing client-side network configuration parameters that are used by an Oracle client to connect to an Oracle server.
to-host file
A file containing work order information exported from a workforce management application other than Field Deployment Manager (FDM), such as Itron’s Endpoint-Link Pro, in a format that allows FDM to import the information into its database.
token
A hardware or software device that performs cryptographic functions and stores public-key certificates, cryptographic keys, and other data. See also private key and public key.
topology
The physical layout of a distribution network infrastructure with specific hierarchical identification of all components.
total available market (TAM)
The total market demand for a product or service, calculated in annual revenue or unit sales if 100% of the available market is achieved.
total cost of ownership (TCO)
A financial estimate intended to help buyers and owners determine the direct and indirect costs of a product or service. It is a management accounting concept that can be used in full cost accounting or even ecological economics where it includes social costs.
total manufacturing cost (TMC)
The total material, labor, overhead, and other expenses associated with the fabrication, assembly, and testing of a product.
TOU
traceroute
A networking utility to track the routes taken by packets across a network. See also ping.
TransferAgent
See SSNIAgent.
transfer request
A request generated by an inventory manager at one warehouse (the to-warehouse) for transfer of an inventory item from another warehouse (the from-warehouse).
transformer
A device in electric utility distribution systems that receives electricity from a feeder and changes the voltage of alternating current (AC) before delivering electricity to the customer’s premises.
Transformer Load Management
A user interface within Itron's Active Smart Grid Analytics (ASA) that leverages SAP Business Intelligence analytics applications to continually monitor and identify under-utilized, over-utilized, and at-risk transformers throughout the distribution system. The kit evaluates kVA utilization, percent loss of life, and top oil and hot spot temperatures, increasing the visibility and management of this utility asset.
transitioning
In the context of OpenWay, the state of an endpoint when it is entering a new version of the same group of which it is a member. An endpoint in transition is tracked to prevent it from being incorrectly counted multiple times.
translation interface module (TIM)
Itron software used to collect time-of-use (TOU) and interval data recorder (IDR) data from meters. Once data is gathered, TIM decode pairs are used to decode designated chunks of that data—per user-defined read item lists—for billing purposes.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
A transport layer protocol within the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol suite. TCP uses retransmission strategy to ensure that data is sent accurately and completely across a network, and that the data is not lost in transmission. Major Internet applications such as the web, email, and File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
transmission mode
The communication method by which an Encoder/Receiver/Transmitter (ERT) module transmits meter reading and related data to a data collection device. ERT modules may be configured to operate in either of two modes—wake-up mode or bubble-up mode.
transparent network substrate (TNS)
A set of Oracle networking architecture services used to facilitate peer-to-peer communication between Oracle components where no machine-level connectivity can occur.
transport layer security (TLS)
An authentication and security protocol widely implemented in browsers and web servers. TLS is based on the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) 3.0 protocol. It uses digital certificates to authenticate both the user and the network. The TLS client uses the public key from the server to encrypt a random number and send it back to the server. The random number, combined with additional random numbers previously sent to each other, is used to generate a secret session key to encrypt the subsequent message exchange.
trap
An asynchronous message sent from a device in the field. Unlike most events, it does not require an application to send a request for data. Rather, the device sends it, as the metaphor suggests, because of specific conditions on the device. An example of a trap is a last gasp (LG).
Trap Forwarder
An obsolete name for Trap Messaging Bridge (TMB).
Trap Messaging Bridge (TMB)
An Itron software component that asynchronously captures, displays, and logs traps from network devices, and allows users to instantaneously view alert notifications from any network device that supports SNMP. Trap Messaging Bridge contains an NMR_Listener feature to capture and forward all communication between applications and the neighborhood area network (NAN) through the Access Point (AP). Trap Messaging Bridge was previously called Trap Forwarder and Trap Receiver. See also Trap Router.
Trap Receiver
An obsolete name for Trap Messaging Bridge (TMB).
Trap Router
An Itron component used by Trap Messaging Bridge (TMB) to enable routing configuration for traps.
trim
To set a bit value from 1 to 0 (used in the context of Virtual Log IDs). Is used to remove a log entry from a Virtual Log.
Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA) Block Cipher
A symmetric block cipher that uses three 64-bit-long keys to encrypt data in three passes. Data is encrypted with the first key, decrypted with the second key, and encrypted again with the third key. Also called Triple Data Encryption Standard, Triple DES, and 3DES.
Triple Data Encryption Standard, (3DES)
See Triple Data Encryption Algorithm (TDEA) Block Cipher.
tri-state checkbox
A type of checkbox employed by the user interface of some applications that indicates an indeterminate state in addition to the two (selected and cleared) provided by a standard checkbox. This third state appears as a square or dash in the checkbox and indicates that its state is neither selected nor cleared.
trouble code
A utility-defined code that a field service representative (FSR) or meter reader uses to indicate a problem encountered while reading a meter or completing a work order. For example, a utility might define a particular code to indicate the presence of a vicious dog on the premises or a locked door that prevents access to the meter.
true power
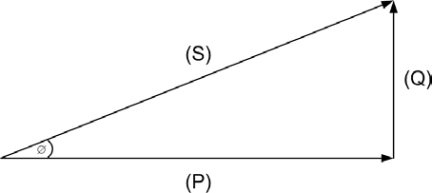
Power dissipated and used by a load. True power is symbolized by the letter P and is measured in watts (W).
The following figure is the Power Triangle. The Power Triangle relates true (P), reactive (Q), and apparent power (S) in trigonometric form.
trust center link key
A 128-bit key used by a Zigbee network to apply encryption to radio frequency (RF) packets being sent between a network trust center device and a Zigbee device being added to the network. The key can be either pre-installed in the Zigbee device or generated and distributed by the trust center device.
TTL
See time to live (TTL).
tunnel
In networking, a tunnel allows the encapsulation of the data of one protocol within another protocol. By using a tunnel, the system passes the encapsulated data over an incompatible network or provides security for transferring data over an untrusted network.
type-length-value (TLV)
Within data communication protocols, optional information may be encoded as a type-length-value or TLV element inside a protocol. TLV is also known as tag-length-value.